Strategic Workforce Planning: The Complete Guide

Table of contents
The ever-shifting tides of the business world demand a dynamic approach to talent management. Strategic workforce planning (SWP) equips organizations with the foresight to navigate these uncertainties. It’s a continuous process designed to ensure your workforce possesses the capabilities needed to translate long-term goals into reality.
What is Strategic Workforce Planning?
Strategic workforce planning (SWP) is a continuous process used by organizations to proactively manage their talent needs. It ensures they have the right people, with the right skills, in the right roles to achieve their business goals, both now and in the future.

Here’s a breakdown of the key aspects of SWP:
- Proactive Approach: It’s not just about filling open positions; it’s about anticipating future skill demands and developing strategies to address them.
- Alignment with Business Strategy: SWP is closely linked to the organization’s overall strategic objectives. The talent strategy is designed to support the execution of the business plan.
- Focus on the Future: SWP utilizes forecasting techniques to identify upcoming skill gaps and develop plans to close them before they hinder progress.
- Data-Driven Decisions: SWP relies on data from HR systems, workforce analytics tools, and industry trends to inform its strategies.
The Issue
The high cost of employee turnover
Employee turnover can be a major financial burden for companies. It’s estimated that replacing a departing worker can cost nearlyone-third of their annual salary. This isn’t just about the immediate financial hit; there’s also a significant loss of valuable knowledge and experience that can take time and effort to rebuild.
This loss of expertise can also erode team morale and create doubts about the team’s ability to perform effectively.
Retention as a key Workforce Planning (WFP) strategy
GoodFirms research highlights the importance of retention, with over 70% of businesses surveyed acknowledging it as a critical issue. Workforce planning (WFP) that prioritizes retention strategies is essential for any organization.
Upskilling as a driver of engagement and retention
One key strategy for boosting employee retention is upskilling. Investing in your workforce’s development shows employees you’re committed to their growth and future within the company.
This can translate into increased engagement and a desire to stay with the organization. Amazon’s commitment to upskilling 100,000 employees exemplifies the potential of this approach.
Beyond the Basics: The Power of Strategic Workforce Planning
SWP isn’t just about filling empty seats. It’s a proactive strategy that yields a multitude of benefits:

Future-Proofing Your Talent Pipeline
By anticipating upcoming skill demands, you can develop targeted recruitment and development programs. This proactive approach reduces the risks pertaining to talent shortages, ensuring a steady stream of qualified individuals to fuel your organization’s growth.
Optimizing Performance
The right talent, strategically placed, is the cornerstone of high-performing teams. SWP helps bridge the gap between strategy and execution by identifying the skills needed to achieve each objective. With the right people in the right roles, your organization can unlock its full potential.
Cost Management Efficiency
SWP empowers you to make informed decisions about your workforce. By identifying areas where upskilling or reskilling current employees can address skill gaps, you can potentially reduce reliance on external hires, leading to significant cost savings.
Boosting Employee Engagement
A well-defined SWP fosters a culture of development within your organization. When employees see a clear path for growth and understand how their skills contribute to the bigger picture, they’re more likely to be engaged, motivated, and invested in the organization’s success.
Strategic Workforce Planning Tools
Technology plays an important role in streamlining your SWP efforts. Here are a few key tools to consider:
Human Resource Management Systems (HRIS)
HRIS data serves as a treasure trove of insights. By delving into this data, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of your current workforce’s demographics, skill sets, and performance metrics.
Workforce Analytics Tools
These advanced tools leverage historical data and industry trends to forecast future workforce needs. Think about having a crystal ball that unveils the specific skills your organization will require in the coming years – workforce analytics can provide just that level of foresight.
Scenario Planning Tools
The business landscape is rarely static. Scenario planning tools allow you to model the impact of different business scenarios on your workforce needs. This empowers you to develop adaptable strategies that can weather unforeseen circumstances.
Strategic Workforce Planning Framework
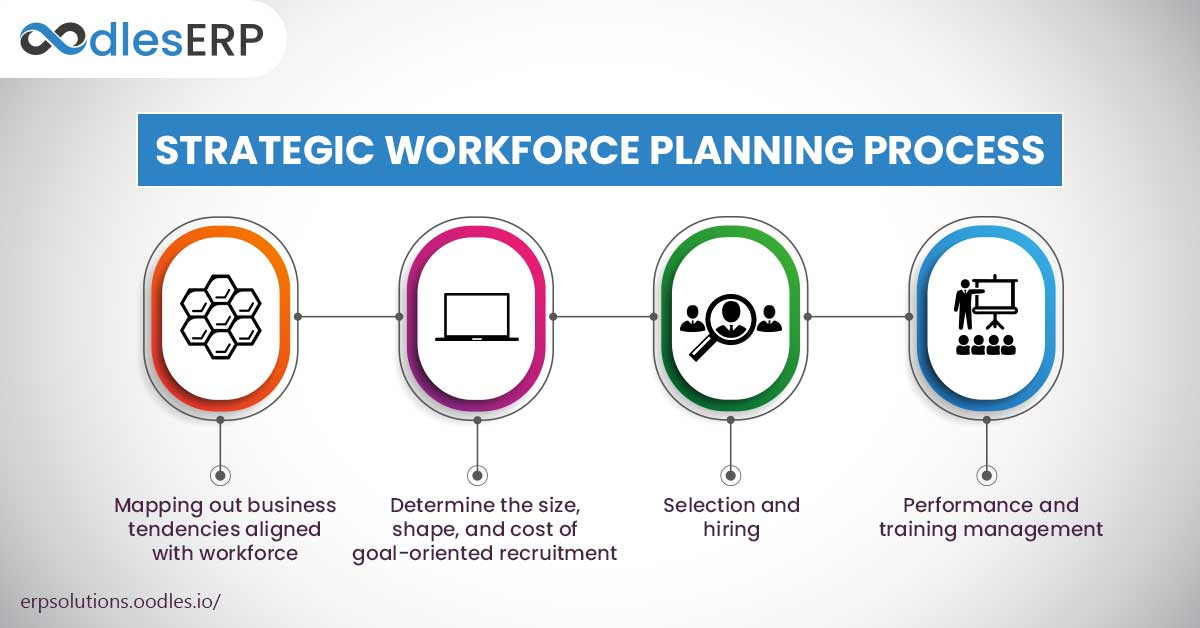
A robust SWP framework serves as the roadmap for your talent management journey. Here’s a breakdown of the fundamental steps involved:
Current State Assessment
Begin by taking stock of your current workforce. Analyze data on skills, demographics, and performance to gain a clear picture of your talent strengths and weaknesses.
Strategic Alignment
Ensure your SWP is inextricably linked to your organization’s overarching business strategy. Understand your strategic goals and how your workforce needs to evolve to support them.
Future-Focused Forecasting
Look beyond the horizon. Utilize workforce analytics and scenario planning tools to identify the skills and talent you’ll need to achieve your future goals.
Bridging the Gap
Once you’ve identified potential skill gaps, it’s time to develop strategies to close them. This might involve targeted recruitment initiatives, internal training programs, or partnerships with educational institutions.
Continuous Improvement
The business world is fluid, and your SWP needs to be as well. Regularly monitor progress, assess the effectiveness of your strategies, and adapt your plan as needed to stay ahead of the curve.
Strategic Workforce Planning Best Practices
While the core framework provides a solid foundation, these best practices will further enhance your SWP’s effectiveness:
Stakeholder Alignment
Gain buy-in from key decision-makers across the organization, including HR, business unit heads, and senior management. A collaborative approach ensures everyone is working towards the same talent goals.
Data-Driven Decisions
Don’t rely on gut instinct; leverage the power of data. Utilize workforce analytics and other data sources to inform your strategic decisions and ensure they’re grounded in reality.
Embrace Agility
The ability to adapt is paramount. Build flexibility into your SWP to accommodate unforeseen changes in the business landscape or the talent market.
Communication is Key
Clearly communicate your SWP to all employees. When everyone understands the organization’s talent goals and their role in achieving them. It fosters a sense of ownership and engagement.
Conclusion
Strategic workforce planning is a powerful tool for securing your organization’s future.
By following the steps outlined above, implementing the recommended best practices, and leveraging the available tools like ProHance, you can develop a comprehensive strategic workforce planning that empowers your workforce to navigate the ever-changing tides of the business world and propel your organization.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is strategic workforce planning (SWP)?
Strategic Workforce Planning is a continuous process that helps organizations ensure they have the right talent with the right skills to achieve their business goals, both now and in the future.
Q2. What is a strategic workforce planning framework?
A SWP framework serves as a roadmap for your talent management journey. Here’s a breakdown of the key steps:
- Current State Assessment
- Strategic Alignment
- Future-Focused Forecasting
- Bridging the Gap
- Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
Q3. What tools can be used to support strategic workforce planning?
Several tools can empower your SWP efforts, including Human Resource Management Systems (HRIS), workforce analytics tools, and scenario planning tools.
Q4. What are some best practices for strategic workforce planning?
Here are some key best practices for SWP: collaboration across the organization, embracing agility, data-driven decision-making, investing in communication, and focusing on measurable outcomes through KPIs (key performance indicators).



