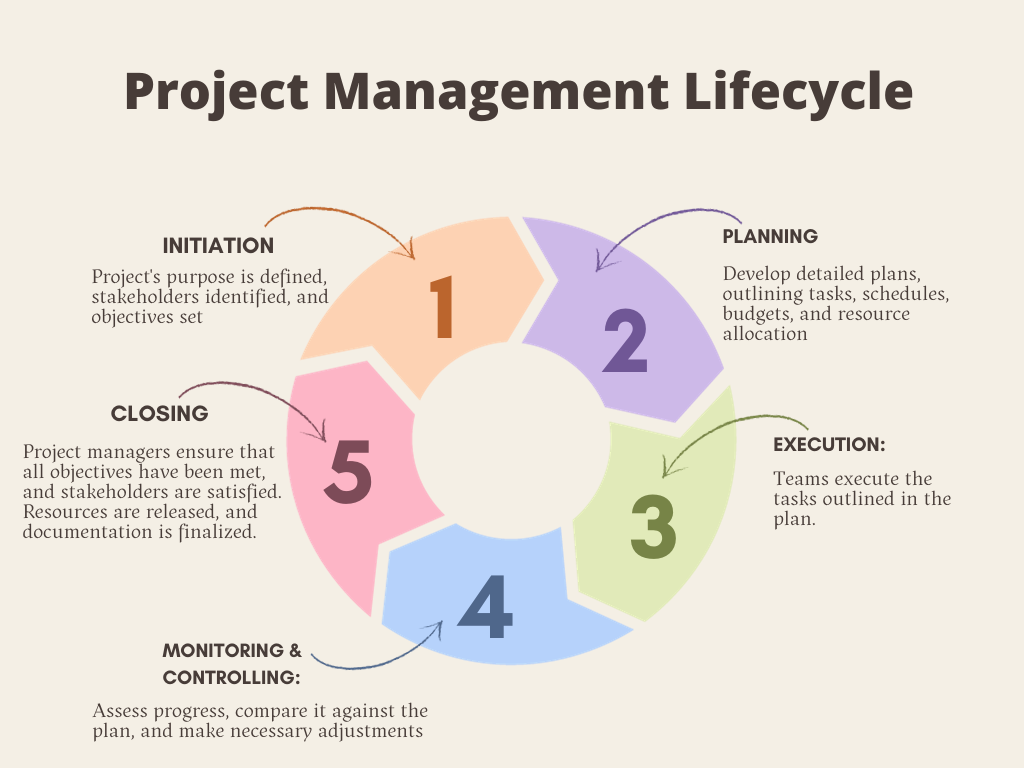
Everything You Need to Know About Project Management

Table of contents
- What Is Project Management?
- What are the most common elements of project management?
- What are the methodologies involved in project management?
- Advanced project management methodologies
- What are The advantages of using Project Management Tools?
- How ProHance Can Help in Advanced Project Management?
- Frequently Asked Questions
Effective project management plays a pivotal role in today’s business landscape. It is a critical component of the business that sets apart thriving organizations from those grappling with chaos and uncertainty.
Without the guidance of a robust project management framework, your business can often drown in several challenges– missed deadlines, ballooning budgets, disjointed teams and dissatisfied stakeholders. And this is never good news for your business.
So, what is project management? What are the elements of project management, and how do you adopt the project management principles correctly?
Let’s find out!
What Is Project Management?
Project management represents the dynamic orchestration of people, processes, and resources to achieve specific objectives within a defined timeframe.
It offers a structured framework, clear communication channels, and meticulous planning, propelling your organization toward successful project outcomes.
History and evolution of project management
Project management has existed since humanity’s earliest endeavors – from the construction of the Great Pyramids to the exploration of new lands. However, it was first recognized as a discipline in modern industry during the 20th-century industrial revolutionization.
What are the reasons that lead to project failure?
Before we discuss in detail about project management, let’s take a look at the reasons why project management fails:
- The lack of defined project objectives and milestones is the reason why 37% of the projects fail.
- 46% of firms have accepted that they do not understand the need or importance of project management.
- According to a report published by the University of Missouri-St. Louis, one-third of projects fail due to the absence of senior management involvement in critical project decisions.
- Yet another leading organization highlights that the 3 primary causes of project failure include inconsistent execution, lack of continuous team improvement and poor scalability.
With proper project management, you can seamlessly iron out the factors that translate into project failure.
So, how exactly are various industries adopting various elements of project management? Let’s take a look!
How do various industries implement project management principles?
- Healthcare: Project management plays a pivotal role in the systemic implementation of life-saving initiatives such as vaccine distribution to hospital expansions alongside limited resource management.
- Marketing and advertising: Project management ensures that campaigns are executed flawlessly, reaching the right audiences at the right time.
- Finance: Project management helps institutions navigate complex regulatory changes and execute strategic investments effectively.
- IT and modern tech: In this rapidly innovative domain, project management ensures that product development stays on track, adheres to budgets, and meets launch deadlines.
Now that you know the relevance of project management, let’s explore the elements of project management and see how to manage a project using these elements/principles.
What are the most common elements of project management?
To understand how to manage a project using project management, you need to know the basic project management principles. These principles include:
Scope Management
In scope management, you’ll need to define and control what will be included and what won’t in a project. It involves setting clear boundaries to prevent “scope creep,” where additional, unplanned work can derail timelines and budgets.
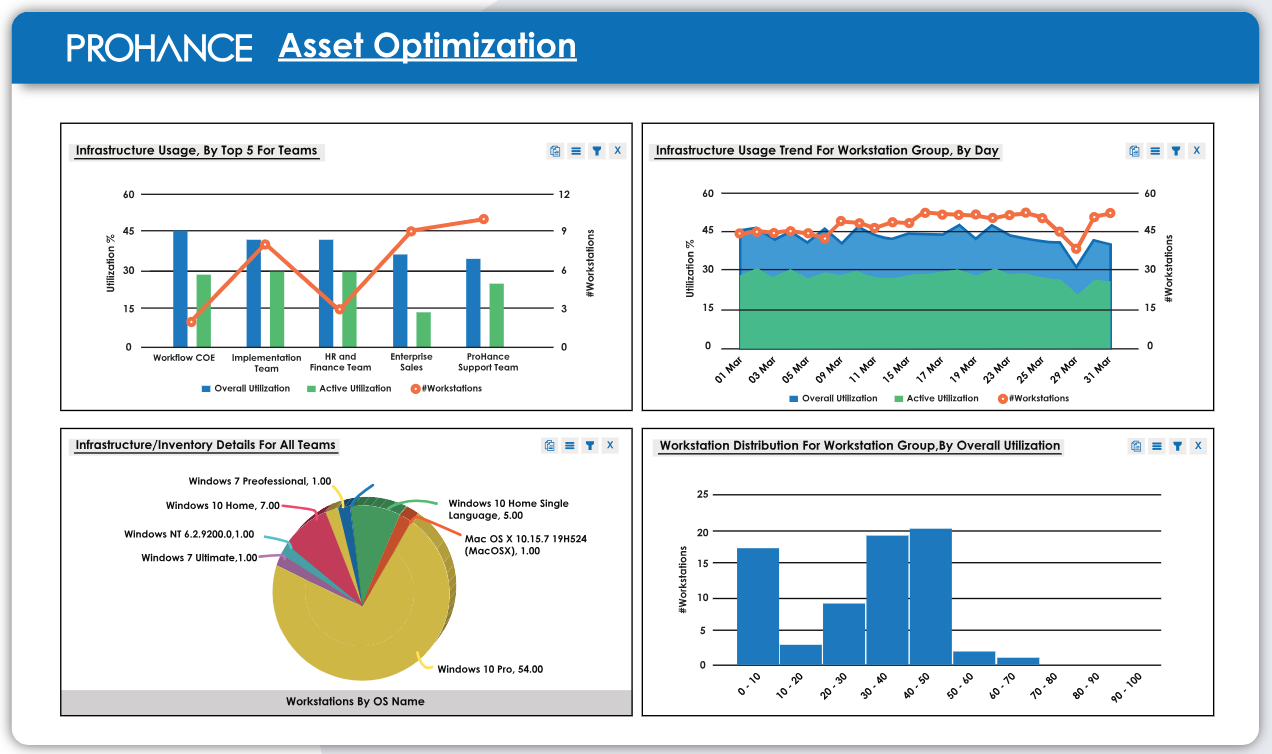
Time Management
Time management is the art of scheduling and organizing tasks to ensure the project stays on track. With proper time management, you can set realistic deadlines, identify critical paths, and diligently adhere to timelines to prevent delays.
Read more: Why Is Time Management Important In The Workplace?
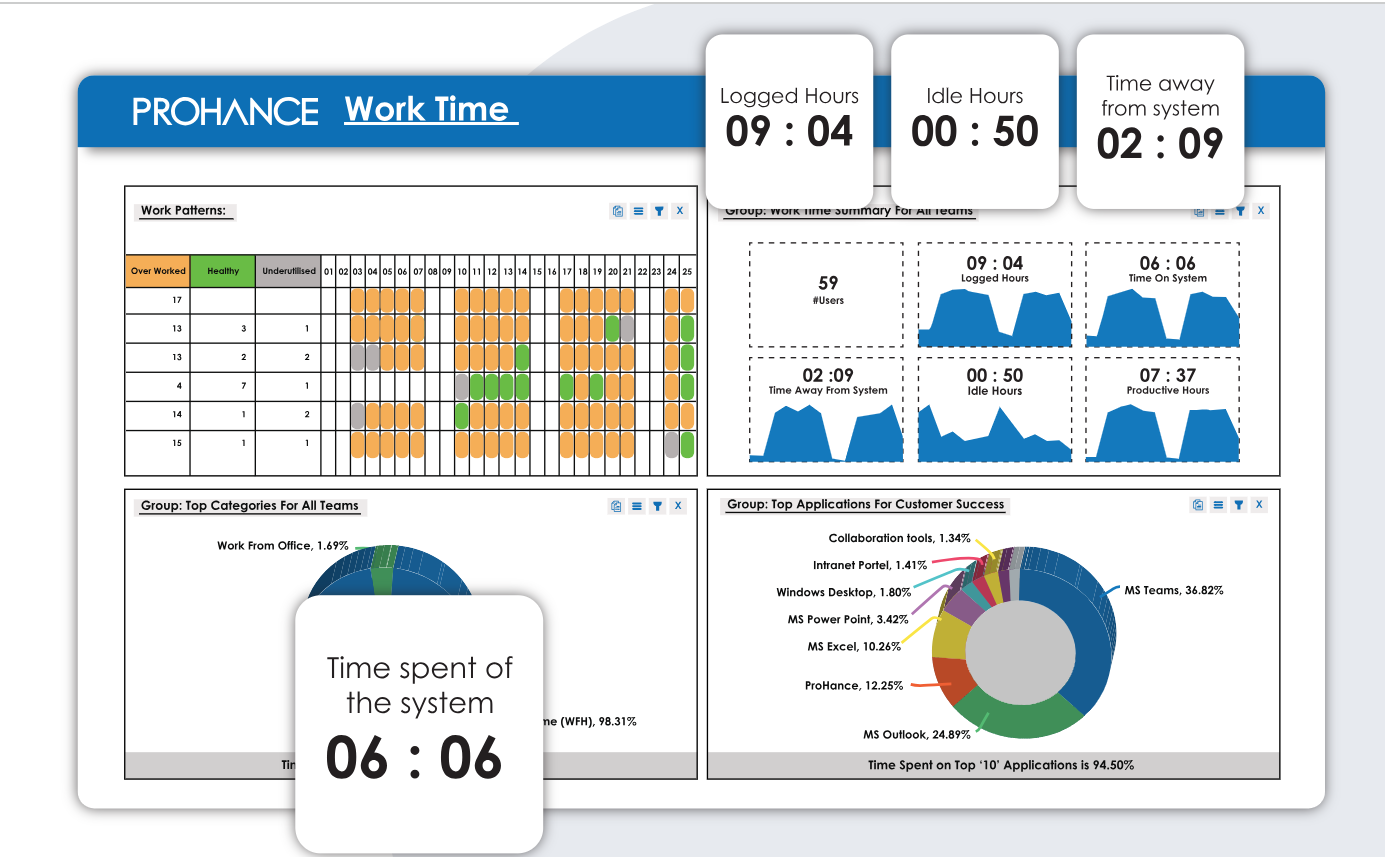
Compare key business metrics against time metrics with the work time module.
Cost Management
Cost management encompasses everything related to the finances of your project throughout the project’s lifecycle– from budgeting to expense monitoring and cost control. Cost management ensures financial resources are allocated wisely to prevent overspending.
Quality Management
Quality management focuses on meeting or exceeding established standards and expectations. It defines quality criteria, ensures the implementation of quality checks, and continually strives for excellence in project deliverables.
Risk Management
Risk management is the art of identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential project risks. In risk management, your team will perform proactive planning to minimize the impact of unforeseen events and uncertainties.
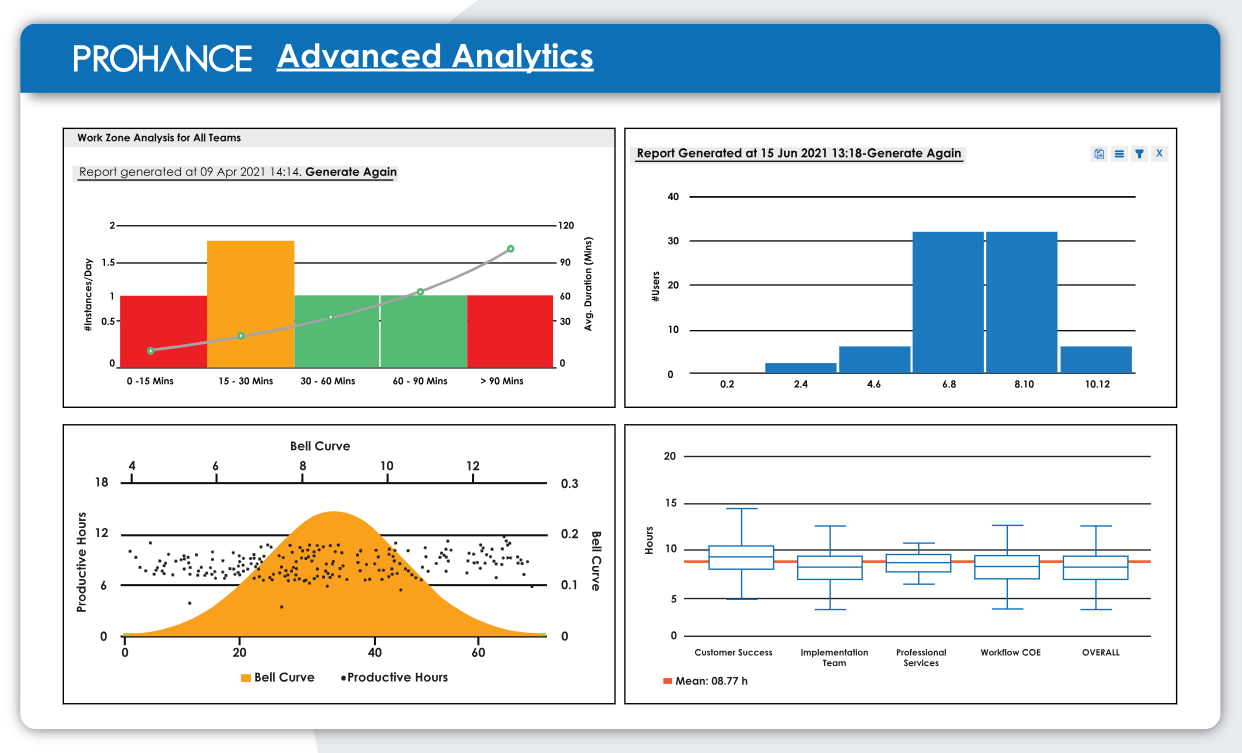
Manage cost, project quality and risk with ProHance’s advanced analytics
Communication Management
Communication management ensures that information flows effectively within the project team and stakeholders. It involves clear, timely, and relevant communication to avoid misunderstandings and keep everyone aligned.
What are the methodologies involved in project management?
Did you know? Poor project management can lead to 12% of valuable resources going to waste. To avoid that, you can adopt one or more of the following methodologies for your projects.
Waterfall Methodology
Waterfall is a sequential project management approach. In the waterfall method, the project workflow follows a structured and linear approach where tasks flow in a manner much like a waterfall’s descent.
Pros:
- Clear and easy-to-follow structure
- Detailed and documented processes
- Well-suited for stable projects
Cons:
- Rigid in adapting to a changing environment.
- Limited stakeholder involvement until the end of the project.
Agile Methodology
In Agile management, projects are divided into smaller iterative and incremental parts. Agile presents flexibility and adaptability, offering a dynamic approach to project execution.
Pros:
- Flexibility
- Continuous stakeholder collaboration
- Quick deliveries
Cons:
- More complex and requires expertise
- Knowledge gaps due to minimal documentation
Scrum Methodology
Scrum in project management focuses on strategizing and collaborating. It is ideal for small, cross-functional teams functioning together efficiently.
Pros:
- Efficient team collaboration
- Transparency
- Adaptability
Cons:
- Strict Roles
- Complex management for large projects
Kanban Methodology
Kanban board functions as your project’s personal assistant, organizing tasks, setting priorities, and ensuring you stay focused on the essentials. Kanban is all about visualizing your workflow and optimizing efficiency.
Pros:
- Clear visual representation
- Improves overall efficiency
- Flexibility
Cons:
- Less defined structure
- Complex dependency management
Lean Methodology
Lean is the Marie Kondo of project management, decluttering processes and eliminating waste. It’s all about maximizing value and minimizing the excess, resulting in streamlined projects.
Pros:
- Elimination of waste
- Continuous improvement
- Customer focused
Cons:
- Resource intensive
- Not suitable for all projects
Advanced project management methodologies
Apart from these common project management methodologies, you can also work with a few advanced methodologies to manage your projects. Each methodology offers unique advantages and challenges, making them suitable for different project scenarios.
Hybrid Project Management
When you’re working with complex projects, you can benefit from blending Agile and Waterfall methodologies. This hybrid approach allows you to leverage the structured planning of Waterfall while incorporating Agile’s adaptability to changing requirements.
Critical Chain Project Management
Critical Chain focuses on resource constraints and buffers to enhance project delivery. By identifying critical resource dependencies and managing them effectively, this methodology reduces project delays and optimizes resource allocation.
PRINCE2 (Projects IN Controlled Environments)
PRINCE2 is a process-driven methodology widely used in government and large organizations. It offers a robust framework for project governance, emphasizing clear roles, responsibilities, and controlled processes.
Earned Value Management (EVM)
EVM integrates project scope, cost, and schedule to track project performance. It provides objective metrics to assess progress and predict project outcomes accurately.
What Are The Advantages Of Using Project Management Tools?
Project management software offers a toolkit of features that simplify the most complex tasks.
Enhanced collaboration
With project management software, teams can work together seamlessly, no matter where they are located. Communication is streamlined, and everyone has access to real-time project data.
Efficiency
These tools automate many repetitive tasks, reducing the risk of errors and saving valuable time. Task assignments, deadline reminders, and progress tracking become effortless.
Improved decision-making
With access to comprehensive project data and analytics, project managers can make informed decisions quickly. This leads to better resource allocation, cost control, and risk management.
How ProHance Can Help in Advanced Project Management?
ProHance is a comprehensive workforce management platform designed to streamline every aspect of your projects.
From resource optimization to predictive analytics, real-time reporting and collaboration tools– ProHance offers a plethora of features that make project management a breeze.
Whether you’re managing a small team or a large enterprise, ProHance has you covered!!
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is the basic purpose of project management?
The fundamental purpose of project management is to plan, execute, and control projects effectively to achieve specific objectives within defined constraints, such as time, cost, quality, and scope. It ensures that projects are completed efficiently and meet stakeholder expectations.
Q2: What is Six Sigma project management?
Six Sigma project management is an approach focused on improving process efficiency and quality by reducing defects and variations. It relies on data-driven decision-making and employs techniques to achieve process optimization and excellence.
Q3: What is a PMO department?
PMO stands for Project Management Office, a department within an organization responsible for standardizing and overseeing project management practices. It provides support, governance, and resources to ensure consistency and successful project execution across the organization.
Q4: What is project methodology?
Project methodology refers to a structured framework or approach that guides how a project is planned, executed, and controlled. It includes processes, tools, and techniques used to manage projects effectively, such as Waterfall, Agile, or Scrum methodologies.
Q5: What is meant by a Gantt chart?
A Gantt chart is a visual project management tool that displays project tasks or activities on a timeline. It illustrates the start and end dates of each task, dependencies between tasks, and the project’s overall schedule, providing a clear overview of project progress.
An example of Gantt Chart template (Source)
Q6: What is a project framework?
A project framework is a structured approach or guideline that outlines the key components and processes necessary to manage a project successfully. It serves as a blueprint for planning, executing, and controlling projects and often includes methodologies, templates, and best practices tailored to the organization’s needs.



