A Definitive Guide to Lean Management

Table of contents
The American business landscape is dynamic and ever-evolving. And you need to make your business operation more efficient than ever to accommodate the ever-evolving customer demands and get a competitive edge in your industry.
- A year ago, 54% of customers had lower customer service expectations compared to their current heightened expectations.
- A significant 76% of customers anticipate that companies should comprehend their specific requirements and anticipations, while 66% are prepared to sever ties with a brand if they perceive themselves as being treated as an impersonal entity rather than as an individual.
- American customers are willing to spend an additional 17% when buying from a company that offers superior customer service.
So, what management approach can you take to enhance the efficiency of your organizational processes and deliver customer experience? Enter Lean Management!
The Lean management system presents a dynamic and potent approach that holds the key to mastering this ever-shifting business terrain.
In this definitive guide, we’ll explore the principles, processes, and benefits of Lean Management, providing valuable insights for businesses aiming to optimize their operations.
Let’s begin with the basics!
What is Lean Management?
Before we decode lean principles and processes, let’s understand what is Lean Management. Also known as Lean, it is a systematic approach aiming to eliminate waste and improve efficiency within an organization.
Rooted in manufacturing but now widely applied across various industries, the Lean management system focuses on maximizing value for customers while minimizing resources.
To explain the concept of lean better, let’s take a look at the Lean management principles.
What are the Five Core Lean Management Principles?
Lean Management is built on five core principles, as articulated by the experts at The Lean Way:
Identify Waste and Inefficiencies
The first principle of Lean is to recognize and eliminate waste in all forms, such as unnecessary processes, overstaffing, and unnecessary tool subscriptions.
Fact: Companies waste approximately 32% to 41% of their software budget on features, tools, or platforms that are unnecessary or go unused.
Value Stream Mapping
Lean organizations meticulously map their value streams to identify areas that need improvement. This involves analyzing the workflows, employee work trends, and other dynamic organizational information from start to finish.
Fact: 54% of employees believe they can save approximately 2 hours of work every day using automation.
Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement effort is at the heart of Lean Management. It involves incremental, ongoing efforts to enhance processes, products, or services.
Fact: Among the 20 companies that were part of the survey, 55% reported returns ranging from $100,000 to $500,000 as a result of enhancements in business process management.
Respect for People
Lean management system fosters a culture of respect for employees, recognizing that they are the key to identifying and solving problems. Engaged, satisfied, and empowered employees are more likely to drive positive change.
Fact: Among workers who experience work-related stress, 41% mention that their stress levels lead to reduced productivity.
Pull System and Just-in-Time (JIT) Production
A pull system is a production method (software tools, applications, etc.) where work is only pulled when there is demand for it. This contrasts with a push system, where work is produced in advance and stored until needed.
In a Lean environment, a pull system ensures that products or services are delivered when the customer needs them, reducing waste and excess inventory.
Fact check: 60% – 73% of data within an organization goes unused by analytics.
Also Read: How Workforce Analytics Is Important in Lean Management
Lean process embodies Continuous improvement to drive greater operational efficiency. So, how do you implement a Lean management system? Let’s find out!
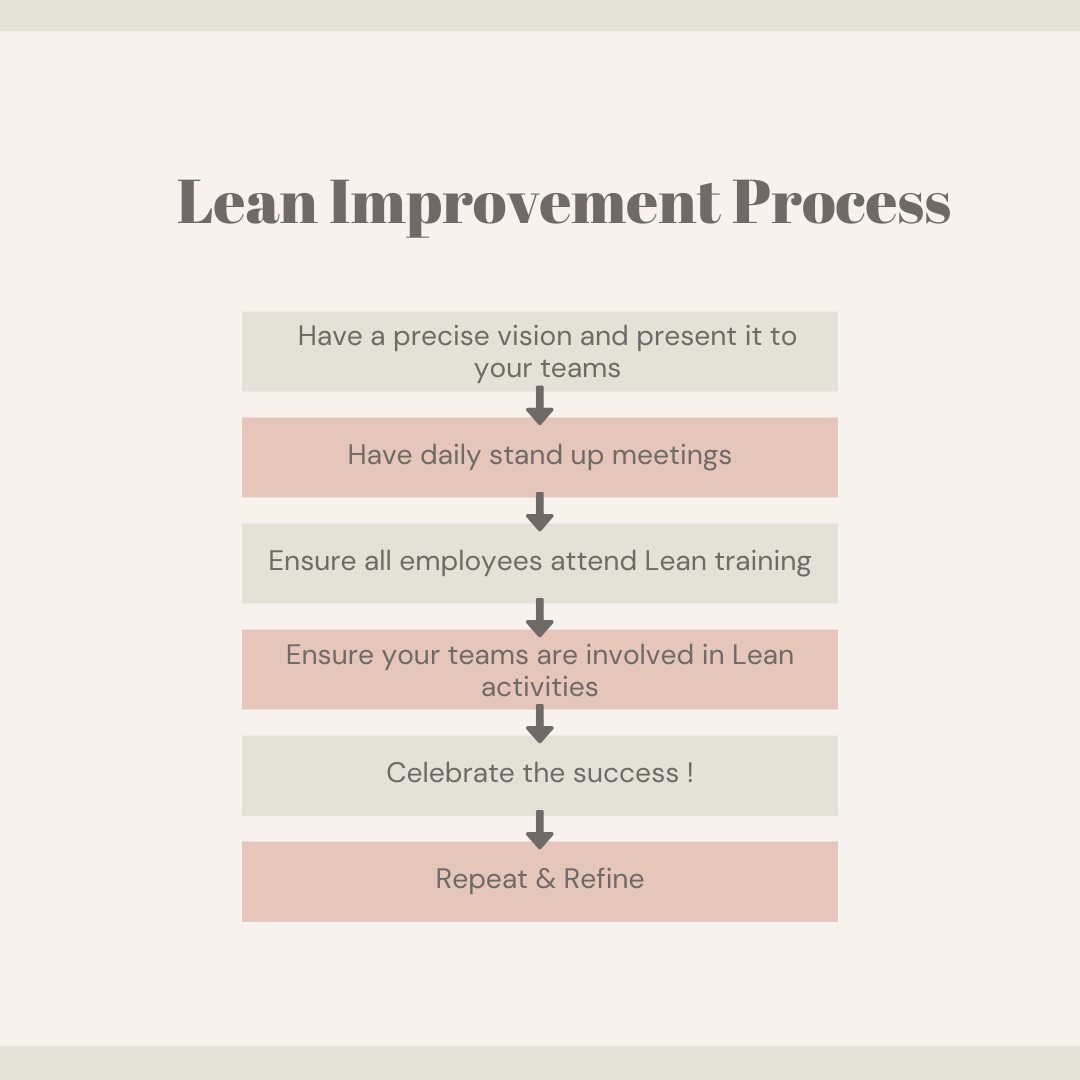
What are the Steps Involved in the Implementing Lean?
A structured lean improvement process is essential for implementing Lean Management effectively. This process typically includes the following steps:
Identify Opportunities for Lean Improvement
The journey starts with recognizing areas where improvements can be made, often involving input from employees at all levels.
- Identifying opportunities for improvement requires a keen eye and a willingness to question the status quo.
- This step often begins with feedback from employees who are closest to the processes in question.
- It’s crucial to create a culture where employees feel comfortable suggesting improvements.
Analyze Current Processes
Understanding the existing workflow involves documenting processes, identifying bottlenecks, and quantifying waste.
By quantifying waste and identifying areas where processes can be streamlined, organizations can target their improvement efforts effectively.
Plan Improvements
Planning improvements involves setting clear objectives and developing a roadmap for achieving them.
This step requires careful consideration of resources, timelines, and potential obstacles. A well-defined Lean management system increases the likelihood of successful improvements.
Implement Changes
Implementing changes can be challenging, as it often requires employees to embrace new ways of working. Effective communication, training, and support are essential during this phase to ensure that changes are embraced and integrated into daily operations.
Monitor and Measure Results
Continuously track the impact of the changes using key performance indicators (KPIs) . If the desired outcomes are not met, you can make adjustments to further refine processes.

Benefits of Lean Management
The adoption of Lean Management principles can result in a wide range of benefits for your businesses. Let’s take a look at the benefits of Lean Management.
- Cost Reduction: By eliminating waste and optimizing processes, Lean reduces operational costs, ultimately improving the bottom line.
- Improved Quality: Enhanced focus on quality control leads to better products or services, increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: Lean management systems streamline operations, allowing organizations to produce more with the same or fewer resources.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Lean’s customer-centric approach ensures that products and services fulfill or exceed customer expectations.
- Positive Workplace Culture: Emphasizing respect for employees and continuous improvement fosters a more engaged and satisfied workforce.
Also Read: The Ultimate Guide to Business Process Management (BPM)
Examples of Lean Management
Let’s take a look at a few companies that have successfully implemented Lean Management Systems.
Toyota
Often considered the pioneer of Lean principles, Toyota has consistently demonstrated the effectiveness of Lean in the automotive industry. They’ve streamlined production processes, reduced waste, and achieved remarkable levels of efficiency.
Toyota’s success with Lean Management serves as a testament to the principles’ universal applicability. While Toyota is in the automotive business, its Lean practices can be adapted and applied by organizations of all sizes and industries, especially IT, Finance, Sales, Consultancy, etc.
Amazon
One of the best Lean process improvement examples is Amazon. The e-commerce giant applies Lean principles to its fulfillment centers. By optimizing processes and minimizing waste, Amazon ensures speedy deliveries while maintaining customer satisfaction.
The company’s focus on Continuous improvement and customer-centricity aligns with Lean principles and has propelled its success.
ProHance: Your Partner in Embracing Lean Management System
In a world where a Lean Management System isn’t just a choice but a strategic imperative, ProHance becomes the cornerstone of your success story.
With ProHance, you gain the power to see your workforce analytics through a magnifying glass, identifying areas of improvement, streamlining processes, and enhancing overall efficiency.
Also Read: What are the use cases for ProHance?
It’s your digital partner in the pursuit of perfection, offering the data-driven clarity needed to make informed decisions and drive Continuous improvement.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: How does Prohance support Lean process improvement?
Prohance offers data-driven insights that help identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and opportunities for improvement. It provides visibility into processes, enabling organizations to optimize workflows and streamline operations in line with Lean principles.
Q2: Can Lean Management be applied to industries other than manufacturing?
Yes, Lean Management principles are adaptable to various industries, including Healthcare, Marketing management, Business consultancy, Technology services, Financial management, and more.



