The Employee Turnover Guide: What It Is And How You Can Manage It

Table of contents
Employee turnover, a prevalent concern in today’s workforce, stands as a pivotal metric for organizational health. As businesses evolve, understanding and managing turnover becomes paramount.
In this guide, we’ll delve into what employee turnover is, ways to calculate it, its costs, types, causes, and crucially, strategies to minimize it using tools like ProHance—a new-age operations enablement & analytics platform equipped with modules tailored for effective management.
What is employee turnover?
Employee turnover represents the rate at which employees leave a company over a specific period. So, is it just a mere headcount of employees leaving the organization?
Not really! It’s an indicator of the company’s attrition rate. This includes the departure of employees for various reasons: seeking better opportunities, personal reasons, retirement, layoffs due to restructuring, or terminations based on performance issues.
Beyond the numerical aspect, turnover involves analyzing the reasons behind departures.
- Voluntary turnover might result from factors like lack of growth opportunities, unsatisfactory work conditions, poor management, or limited work-life balance.
- Involuntary turnover, on the other hand, could arise from organizational changes, downsizing, or performance-related issues.
What is a Good Turnover Rate?
Determining an ideal turnover rate depends on several factors, including industry norms, job market dynamics, and the organization’s unique circumstances.
Generally, a lower or healthy turnover rate signifies stability and contentment among employees. However, certain industries, such as retail or seasonal work, might experience naturally higher turnover rates.
A healthy turnover rate is relative, but benchmarking against industry standards or historical data can offer insights. For instance, tech companies might experience higher turnover due to the competitive landscape and the demand for specialized skills.
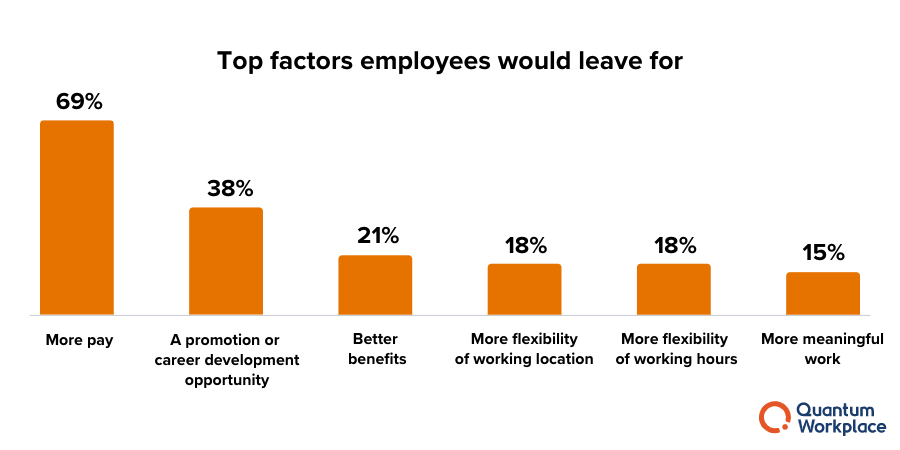
Analyzing turnover trends over time helps in setting realistic targets and identifying potential issues.
- Typically, businesses encounter an average annual turnover of around 18% within their workforce.
- On average, companies can anticipate a 6% loss of their workforce due to layoffs or dismissals resulting from underperformance. This category of turnover is termed involuntary turnover.
- The average annual turnover rate for top-performing employees is 3%. However, in leading companies known for excellence, this figure tends to approach zero.
What are the various types of employee turnover?
Understanding the types of turnover types sheds light on the reasons behind employee departures:
Voluntary Turnover
Employees leave the company by choice, often seeking better opportunities, career growth, or a more conducive work environment. With accurate appraisals, shift differentials, paid training, etc, you can reduce employee turnover.
Involuntary Turnover
Employees are let go or due to performance issues, layoffs, or organizational changes. Involuntary turnover is mostly done during cost-cutting, acquisitions, or mergers.
Functional Turnover
Underperforming employees voluntarily leave, which could sometimes benefit the organization.
Dysfunctional Turnover
High-performing individuals leave, causing a loss for the organization. Dysfunctional turnover mostly results from a lack of growth opportunities, inequitable work distribution, and inadequate appreciation for the work done.
Recognizing these distinctions helps in strategizing retention efforts and addressing specific issues contributing to turnover.
How to Calculate Employee Turnover Rate?
To calculate employee turnover, you need to use a simple formula: divide the number of departures by the average number of employees over a specific period, then multiply it by 100 to obtain a percentage.
For a deeper understanding, you can leverage tools like ProHance’s Work Time Tracking Module, which provides real-time data and insights of managing employee workload. By analyzing trends across departments or job roles, you can pinpoint areas needing attention.

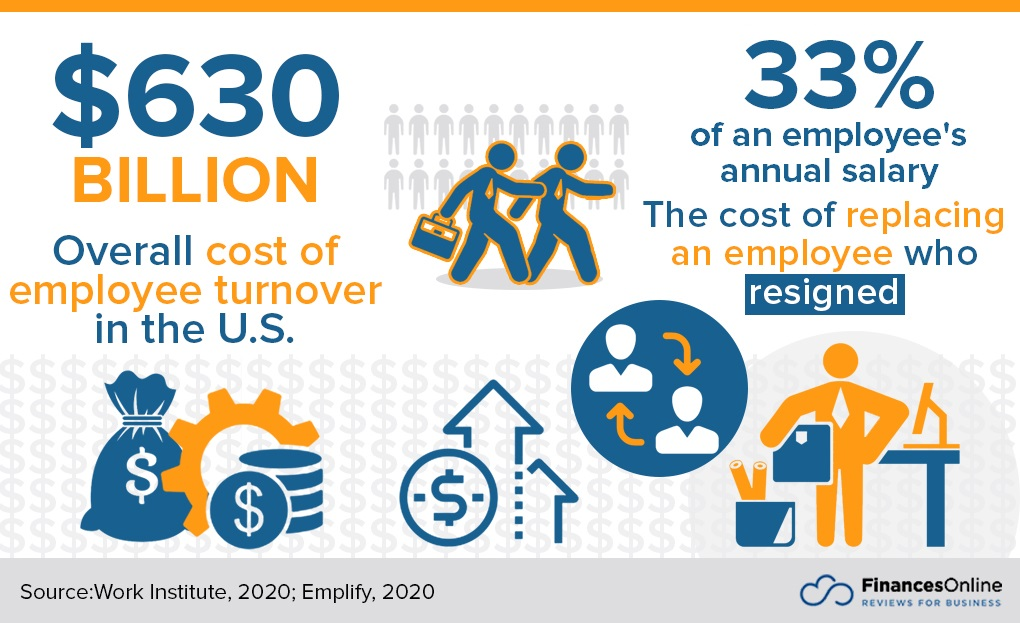
The Cost of Employee Turnover
The cost of employee turnover encompasses various direct and indirect expenses incurred by an organization when employees leave and need to be replaced.
Replacing a single employee can incur expenses ranging from 50% to twice the individual’s salary. For instance, the departure of an employee earning $80,000 annually could potentially cost the organization up to $160,000.
Beyond the immediate costs of recruiting and training new hires, there are several nuanced financial implications involved in turnover.
- Advertising and Marketing: Costs associated with posting job listings on various platforms, including job boards, social media, and recruitment agencies.
- Screening and Interviewing: Time and resources spent on reviewing resumes, conducting interviews, and assessing candidates.
- Orientation and Training Programs: Costs involved in acclimating new hires, providing initial training, and familiarizing them with company policies, procedures, and culture.
- Mentoring and Supervision: Resources allocated for mentorship programs or supervisors dedicating time to guide new employees.
- Decreased Productivity: During the transition period, new hires often take time to reach the same level of productivity as their predecessors. This productivity gap translates into lost output and efficiency.
- Impact on Team Performance: Departures might disrupt team dynamics, affecting overall team performance and collaboration.
- Loss of Intellectual Capital: Departing employees take their institutional knowledge, expertise, and relationships with clients or stakeholders with them, resulting in intangible losses for the organization.
- Skills Gap: Finding replacements with the same skill set can be challenging, leading to potential skills gaps within teams.
- Team Morale: High turnover can negatively impact the morale of remaining employees, causing stress, uncertainty, and decreased engagement.
- Replacements’ Morale: New hires might be discouraged by frequent turnover, affecting their motivation and commitment to the organization.
- Administrative Tasks: Processing paperwork, managing benefits, and handling exit formalities incur administrative costs.
- Compliance and Legal Expenses: Ensuring compliance with labor laws, severance pay, and potential legal fees related to terminations or disputes.
- Client Relationships: If departing employees had direct client relationships, turnover could affect client satisfaction and relationships, potentially leading to customer churn.
- Repeat Costs: If new hires don’t work out and leave shortly after joining, organizations face the same recruitment and training expenses, amplifying the overall cost of turnover.
Causes of Employee Turnover
The causes of employee turnover are diverse and multifaceted, stemming from a range of workplace, personal, and organizational factors. Understanding these causes in-depth is crucial for devising effective strategies to mitigate turnover rates.
Lack of Growth Opportunities
Employees often seek opportunities for career advancement and professional development. When organizations fail to offer avenues for growth or clear paths for progression within the company, employees might feel stagnant in their roles.
This lack of upward mobility or career advancement can result in dissatisfaction and prompt them to seek opportunities elsewhere.
Poor Work-Life Balance
An imbalance between professional responsibilities and personal life can significantly impact an employee’s well-being.
Continuous overtime, unrealistic workload expectations, or a culture that doesn’t respect personal time can cause burnout and diminish job satisfaction. Employees seeking a healthier balance may opt to leave for organizations promoting better work-life equilibrium.
Inadequate Recognition and Reward
Recognition and appreciation for contributions are fundamental to employee motivation. When employees feel their efforts go unnoticed or unrewarded, it can result in a feeling of undervaluation.
Lack of acknowledgment or tangible rewards for hard work can diminish morale and decrease loyalty to the organization.
Toxic Work Environments
Negative workplace cultures characterized by gossip, bullying, favoritism, or lack of psychological safety create stressful and demotivating environments.
Employees subjected to such toxicity are more likely to seek employment elsewhere, searching for a healthier and more supportive workplace culture.

Poor Management and Leadership
Ineffective leadership and poor management practices can significantly impact employee turnover. Managers who lack communication skills, fail to provide guidance, micromanage excessively, or show favoritism can alienate their teams.
A disconnect between leadership and employees’ needs can lead to dissatisfaction and disengagement.
Compensation and Benefits
Competitive compensation packages and benefits play a crucial role in employee retention. When employees perceive their compensation as inadequate compared to industry standards or their efforts, they might be inclined to explore other opportunities offering better financial rewards.
Job Fit and Alignment with Company Culture
A mismatch between an employee’s skills, values, and the organization’s culture or job role can lead to dissatisfaction.
Employees who don’t resonate with the company’s ethos or find themselves in roles that don’t align with their strengths might seek positions that better fit their aspirations and values.
Lack of Support and Resources
Insufficient resources, whether it’s technology, training, or adequate support from management, can hinder employees’ ability to perform their jobs effectively.
Feeling unsupported or ill-equipped for their roles can lead to frustration and disengagement, prompting employees to seek environments where they feel better equipped and supported.
How to Reduce Employee Turnover?
Reducing turnover requires a multifaceted approach that combines data-driven insights and empathetic strategies:
Implement Effective Onboarding and Training Programs
Smooth onboarding processes and comprehensive training programs play a crucial role in acclimating new hires to the company culture and their roles. Investing in structured onboarding helps employees feel welcome, informed, and equipped to excel in their positions from the start.
Companies boasting effective onboarding procedures witness an 82% enhancement in retaining new hires and a surge of over 70% in productivity.
Create Opportunities for Career Development
Establish clear paths for career progression within the organization. Providing opportunities for skill development, training, mentorship programs, and advancement encourages employees to envision a future within the company, boosting retention.
Enhance Work-Life Balance
Foster a healthy work-life balance by providing flexible work schedules and remote work options (if feasible) and encouraging your employees to take breaks and vacations.
Supporting employees in maintaining a balance between work and personal life leads to higher job satisfaction and loyalty.
Recognize and Reward Contributions
Implement recognition programs that acknowledge and appreciate employees’ efforts and achievements.
Regular feedback, public acknowledgment, bonuses, or non-monetary rewards reinforce a culture of appreciation, boosting morale and engagement.
Cultivate a Positive Work Environment
Ensure a supportive and inclusive workplace culture where employees feel valued, heard, and respected. Encourage open communication, address conflicts promptly, and promote teamwork and collaboration.
Emphasize psychological safety to allow employees to share their opinions, thought-process and concerns without fear of retribution.
Invest in Leadership Development
Provide training and resources for managers to improve their leadership and communication skills. Effective leadership positively influences team dynamics, morale, and employee satisfaction, directly impacting turnover rates.
Competitive Compensation and Benefits
Ensure that compensation packages align with industry standards and adequately reward employees for their contributions. Offering competitive salaries, bonuses, health benefits, retirement plans, and additional perks can attract and retain top talent.
Enhance Employee Engagement
Engaged employees are highly likely to stay committed to their roles and the organization. Regularly solicit feedback, involve employees in decision-making processes, and create opportunities for social interaction and team building to boost engagement.
Provide Adequate Resources and Support
Equip employees with the proper tools, resources, and support to excel in their roles. Address concerns promptly, provide professional development opportunities, and foster a culture of continuous learning.
Utilize Data-Driven Insights
Leverage tools like ProHance’s Analytics Module to gather and analyze data on employee engagement, productivity, and satisfaction.
Data-driven insights help identify trends and areas needing improvement, enabling informed decision-making to address turnover issues proactively.
Exit Interviews and Feedback Analysis
Conduct exit interviews to understand and analyze the reasons behind departures. Analyze feedback to identify recurring themes or issues contributing to turnover and use this information to implement targeted improvements.
Wrapping up
Recognizing the causes of turnover, from lack of growth opportunities to toxic work environments, is essential for implementing effective strategies to reduce it.
You need to prioritize fostering a positive workplace culture, providing growth opportunities, recognizing employee contributions, and ensuring an employee healthy work-life balance to retain talent and maintain stability.
In this pursuit, leveraging technological solutions like ProHance becomes invaluable. ProHance’s comprehensive modules, including Workflow, Advanced Analytics, and Asset Optimization, offer a robust platform for organizations to gain real-time insights into their operations.
It enables data-driven decision-making, identifies inefficiencies, and provides actionable insights to address issues contributing to turnover.
The utilization of ProHance’s Work Time Tracking Module simplifies the calculation of turnover rates, offering precise analytics and trends that pinpoint areas requiring attention.
Its capacity to gather data on productivity, employee engagement, and workflow efficiencies empowers organizations to proactively manage and mitigate turnover.
By embracing tools like ProHance, companies can not only streamline operations but also create a positive environment that offers employee satisfaction, engagement, and growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. How do you calculate the employee turnover rate?
Calculating the employee turnover rate involves dividing the number of departures/resignations by the average number of employees over a specific period and multiplying it by 100 to get a percentage.
Q2. What is the cost of employee turnover?
The cost of employee turnover extends beyond recruitment expenses and includes lost productivity, training costs for replacements, and the impact on team morale and productivity. Quantifying these costs is essential for understanding the full financial impact on the organization.
Q3. What is a healthy turnover rate?
A healthy turnover rate depends on industry benchmarks and the organization’s context. It’s a rate that balances necessary departures for growth and internal mobility while minimizing excessive turnover that indicates issues within the organization.



