What is Payroll Management and How to Manage Payroll?

Table of contents
- What is Payroll Management?
- How To Manage Payroll
- 2.1. Apply for an Employer Identification Number (EIN)
- 2.2. Understand and Comply with Wage Regulations
- 2.3. Describe Your Payroll Policy and Procedures
- 2.4. Make use of a time-tracking system
- 2.5. Keep an eye on your cash flow
- 2.6. Spend money on a Payroll Manager/Point Person
- 2.7. Keep Employee and Payroll Records
- Payroll Management Software
- Payroll Management Process
- Payroll Management System
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 5.1. What is the role of a workforce scheduler in scheduling management?
- 5.2. How does workforce management scheduling software differ from traditional scheduling methods?
- 5.3. How can workforce management scheduling benefit my business?
- 5.4. How can I overcome the challenges of workforce management scheduling?
Payroll errors can happen more quickly than you think. Consider the employees whose only source of income is their monthly salary. Consider what would happen if the salary was not paid correctly or if it was not released on time. Such irregularities can have a negative impact on employee morale and, as a result, business productivity.
While it is critical to ensure accurate and timely salary payment, it is also critical to follow various laws and regulations such as labour law, PF, PT, and other statutory compliance. Non-compliance with these laws may result in serious legal and financial consequences.
To ensure that your employees are happy and that you are in compliance with the law, you must first understand what payroll is and how to run payroll effectively. We’ll start with the fundamentals of payroll.
What is Payroll Management?
In a nutshell, payroll management refers to the administration of a company’s employee financial records. This includes information about the employee’s salary, incentives, bonuses, deductions, and net pay. An employer is required by law to maintain and keep these records. Non-compliance with Income Tax laws regarding employee records may result in legal consequences.
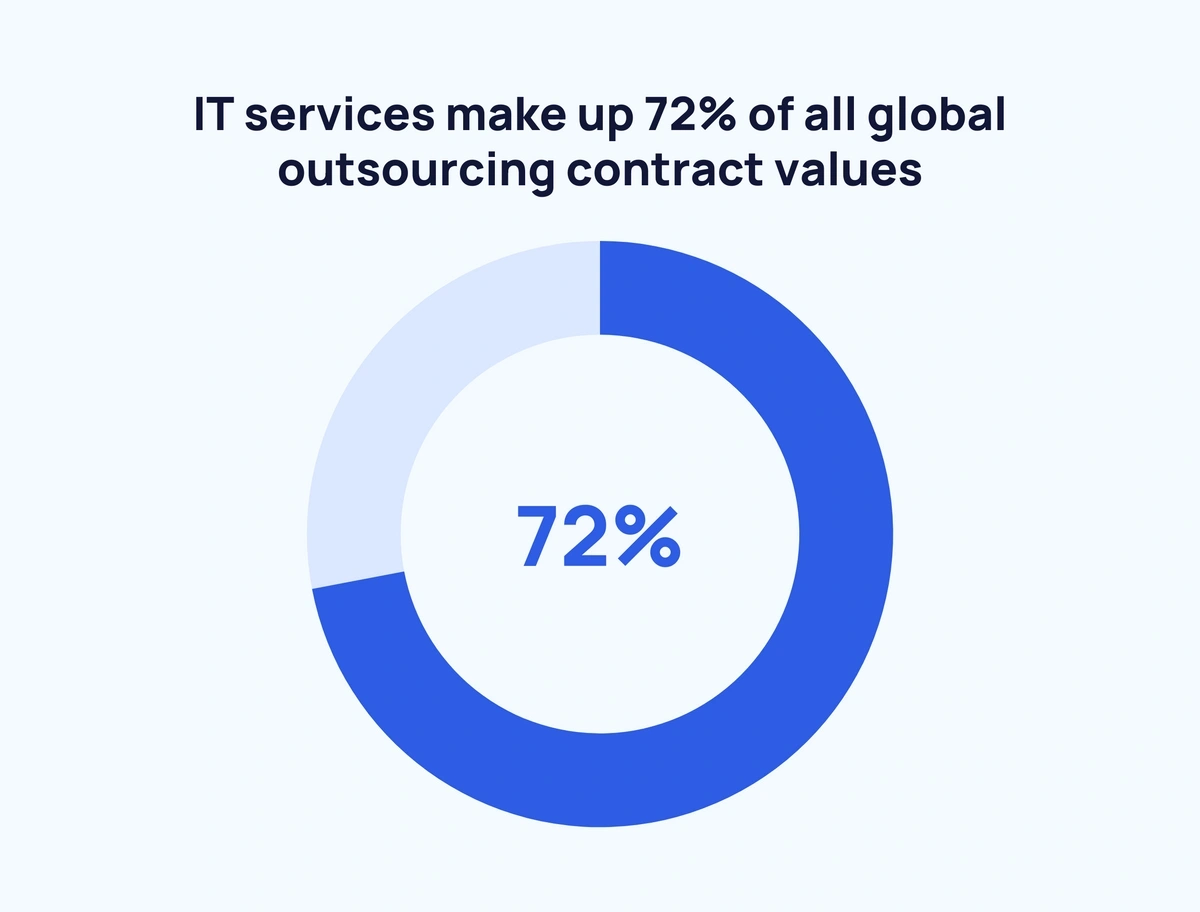
Source- https://explodingtopics.com/blog/outsourcing-stats
How To Manage Payroll
Let’s explore the key steps in payroll management.
Apply for an Employer Identification Number (EIN)
You will need an Employer Identification Number (EIN) before you can begin paying employees. Your EIN, like your Social Security number (SSN), is a way for your small business to be identified for tax purposes.
Most small business owners, require an EIN before they can apply for licences, file payroll taxes, or even open a bank account. Depending on where your company is located, you may need to obtain a state-level EIN in addition to your federal EIN.
Understand and Comply with Wage Regulations
Whatever the case may be, your business must comply with both federal and state laws. This means you or someone in your organisation, must understand your legal and financial obligations as an employer.
Check that you’re paying the correct employment taxes/FICA taxes (i.e., Social Security and Medicare), the correct local and state taxes, and the correct income tax per employee. Check your payroll process to ensure that every employee is paid correctly and on time. Check your payroll tax deposits to ensure they are made on a regular basis in accordance with your tax liability.
Describe Your Payroll Policy and Procedures
Before you run your first payroll, you should create a standard payroll policy. This ensures that everyone, from management to HR to your employees, understands how payroll works, when the payroll period is, how much they can expect to take home, and how benefits like leaves, overtime, etc. are paid.
Make use of a time-tracking system
If you pay hourly rates, a timekeeping system is an excellent way to manage your employees’ productivity and calculate their wages. It is critical to have a time-tracking system that is both simple to use and difficult to manipulate. There are numerous timesheet solutions available, including systems that integrate directly into your payroll system for even more accurate data across the board.
Keep an eye on your cash flow
Every business owner’s worst nightmare: not having enough cash to pay your employees. If you are consistently short during the payroll period, reviewing your cash flow may help you identify the source of the problem. Monitoring your cash flow will assist you in identifying potential payroll issues such as overstaffing or overpaying. During financially stressful times, try delaying a vendor payment or collecting outstanding customer payments before resorting to more extreme cash flow management tactics such as delaying wages or cutting back on expenses.
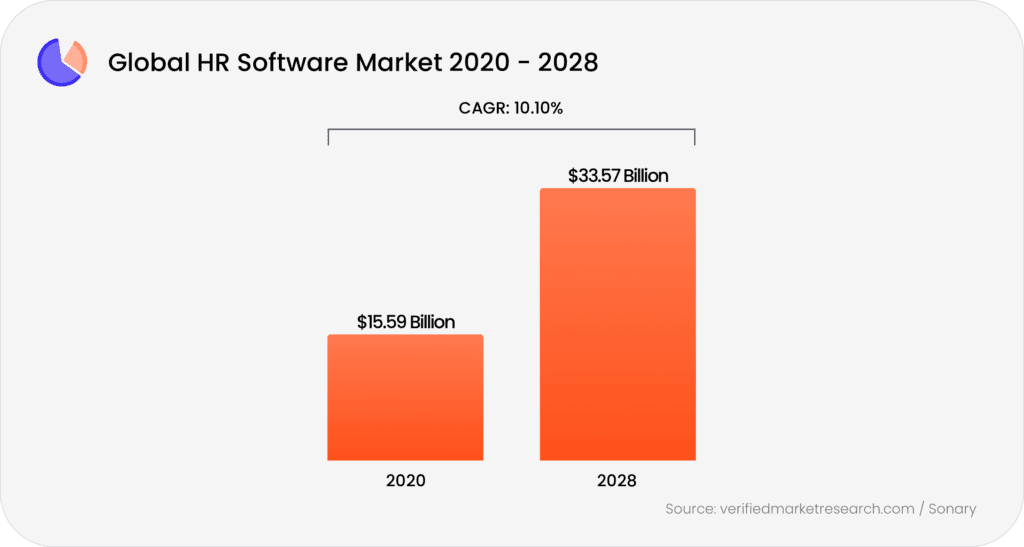
Source- https://www.symmetrical.ai/blog/payroll-statistics
Spend money on a Payroll Manager/Point Person
Payroll can be a difficult task, especially for medium- to large-sized businesses, so it’s no surprise that many companies choose the simplest yet most dependable option: hiring a professional payroll manager.
Instead of devoting hours of your time to payroll, why not hire someone who can do it better and faster so you can focus on running your business? If hiring full-time payroll staff is out of the question, consider hiring a freelancer or simply delegating the task to one of your most skilled and trusted employees.
Keep Employee and Payroll Records
Both the federal and state governments have laws requiring the retention and storage of payroll records in case government agencies require access to that information. You cannot dispose of time cards for active employees for at least two years, and any payroll information regarding paid wages for at least three years. There are also laws that govern the disposition of payroll records following termination.
Also Read: Optimizing Work Efficiency by Reducing App Toggling for Enhanced Productivity
Payroll Management Software
Let’s take a look at payroll management software solutions.
QuickBooks Payroll– QuickBooks is a well-known accounting programme that also includes a payroll management feature. It is simple to use and can assist you in calculating and processing employee salaries, taxes, and deductions.
Gusto– Gusto is a cloud-based payroll solution known for its ease of use and simplicity. It is ideal for small businesses because it automates payroll tasks and assists with tax filings.
ADP Workforce Now– ADP is a well-known company that provides a complete payroll and HR solution. ADP Workforce Now serves businesses of all sizes, from small businesses to large corporations.
Paychex Flex– Paychex Flex is another well-known name in payroll services. Paychex Flex is their payroll processing, tax compliance, and employee benefits management software.
Xero Payroll– Xero is a cloud-based accounting software with payroll capabilities. It is intended for small to medium-sized businesses and seamlessly integrates with Xero’s accounting features.
Payroll Management Process
Let’s take a deep dive into the complexities of payroll management, unravelling its various stages and best practices for seamless employee compensation and compliance.
Employee information should be gathered and updated on a regular basis
Social Security numbers, tax withholding certificates, benefit enrollment deductions, and worker classifications are all required for every employee.
Also Read: Unlocking Efficiency: Your Guide to Tackling Overtime in BPO and IT Companies
Employees are rewarded
In most cases, employers can pay employees by cheque, direct deposit, or pay card, but certain states have laws that prohibit employers from using electronic or alternative pay.
Calculate your gross pay
Employers must log the total hours worked by employees and multiply them by their hourly rate to calculate gross pay for non-exempt or hourly workers. Exempt and salaried workers have it a little easier. To get the answer, divide the annual salary by the number of pay periods.
Keep accurate payroll records
According to the federal government, businesses must keep payroll records for at least three years. Some states have significantly more stringent standards.
Determine your net compensation
Net or take-home pay is calculated after deducting any pre-tax payments for benefits or retirement plans from gross income. Withhold federal income tax, FICA taxes, and any other applicable state or local taxes and withholdings. Finally, deduct some types of benefits, retirement plans, and wage garnishments after taxes, if necessary.
Payroll Management System
Let’s dive into a thorough examination of the payroll management system.
Management of Employee Data
- Employee information such as names, addresses, and contact information should be stored and organized.
- Keep track of your employment history, job titles, and pay rates.
Salary and Benefits
- Employee salaries, wages, and overtime payments must be calculated and managed.
- Handle various types of compensation such as bonuses, incentives, and deductions.
Tax Breaks and Compliance
- Calculate and withhold taxes automatically, including federal, state, and local taxes.
- Ensure that all tax laws and regulations are followed.
Payroll Administration
- Paychecks are processed and distributed, or direct deposits are made possible.
- Create employee pay stubs and reports.
Attendance and Time
- Keep track of employee attendance and working hours.
- To automate time entry, and integrate with timekeeping systems.
Conclusion
Most payroll management systems are cost-effective because they can operate remotely and save data in the cloud, which we can access from anywhere. With an active subscription from payroll software providers, we can keep the database up to date. Payroll Management systems use the least expensive hardware to process payroll, which saves a significant amount of money.
When the payroll system is running, any organization can benefit from payroll software by improving performance and lowering costs and errors. Choose the best Payroll Management software that is secure because it contains sensitive information about your company and its employees.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is the significance of accurate payroll management in the business world?
Payroll management is critical for businesses for a variety of reasons. First and foremost, it ensures that employees are paid correctly and on time, which is critical for job satisfaction and motivation. Payroll accuracy also aids a company’s reputation and ability to retain talent. Payroll management is also important for adhering to tax laws and labour regulations. Payroll errors can result in legal issues and financial penalties.
Payroll management that is accurate also helps a business budget effectively. You can plan your finances more effectively if you know how much you’re spending on employee salaries, benefits, and taxes. Furthermore, a well-organized payroll system simplifies record-keeping and reporting, making it easier to track expenses and pay employees.
Q2. How does payroll software differ from manual payroll processing?
Payroll software and manual payroll processing are vastly different. Many payroll-related tasks are automated by payroll software, whereas manual processing requires human effort and calculations. Here’s how they stack up:
Payroll Software
Automation- Payroll software automatically calculates wages, taxes, and deductions, reducing the risk of errors.
Efficiency- It processes payroll more quickly, saving time and effort.
Compliance- It assists businesses in remaining compliant with tax laws and labour regulations by automatically updating tax rates and rules.
Manual Payroll Processing
Labor-Intensive- Manual calculations are required, which are time-consuming and prone to error.
Risky- Errors in manual processing can result in overpayments, underpayments, or legal issues.
Compliance Issues- Keeping up with changing tax laws can be difficult and may result in compliance issues.
Q3. How frequently should payroll be processed, and what is the employee payroll schedule?
The frequency and schedules for payroll processing can vary, but they should be clearly defined and communicated to employees. Payroll is typically processed weekly, biweekly, semi-monthly, or monthly. The decision is influenced by business requirements as well as state or local labour laws.
Weekly- Employees are paid once a week, usually on the same day of the week.
Bi-weekly- Paychecks are issued every two weeks, typically on a set day, such as every other Friday.
Semi-monthly- Pay is distributed semi-monthly, usually on the 15th and last day of the month.
Monthly- Employees are paid on a monthly basis, usually at the end of the month.


