Effects of Work Stress and Burnout on Employees

Table of contents
The modern workplace is a dynamic environment that offers many opportunities for personal and professional development. However, work stress and burnout may be a deadly enemy that lurks behind the surface of productivity and advancement. These interrelated factors can have a substantial effect on workers’ physical and emotional health in addition to their working lives.
Before we discuss more on employee burnout, we’ll touch on some important stats:
- According to a recent American Psychological Association poll of 1,501 employees, 79% of them were burnt out at their current jobs.
- According to a recent American Psychological Association survey, 66% of professionals report that they frequently miss at least one meal a day as a result of stress and work-related obligations.
- Companies are expected to lose $223 billion annually due to burnout in terms of missed productivity and medical costs.
What is work stress?
Work stress is the emotional and physical pressure experienced as a result of the demands and pressures of our jobs. It arises when the perceived expectations on us, whether real or imagined, exceed our ability to cope. This can be triggered by various factors that create an imbalance between the demands placed on us and the resources we have available to manage them effectively.
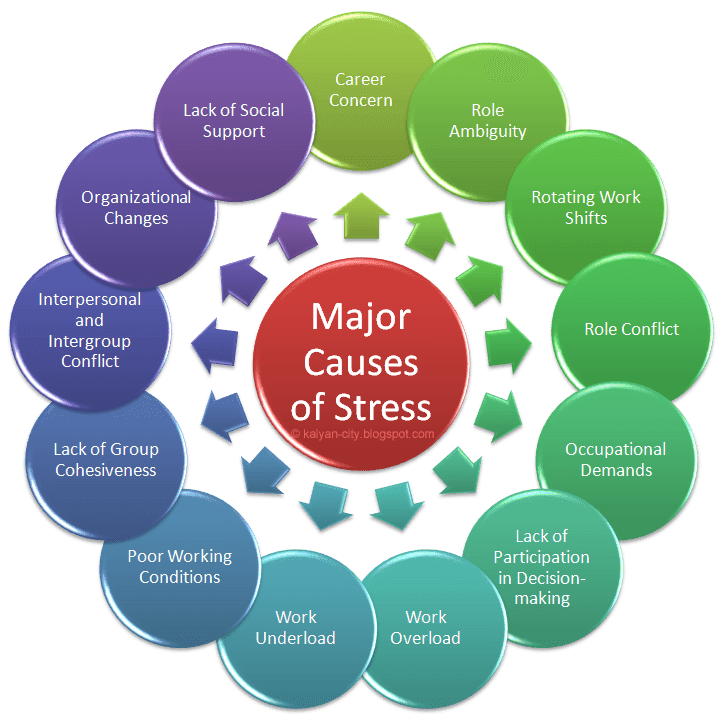
What are the causes of work stress?
Work stress, a prevalent issue affecting individuals and organizations worldwide, stems from a complex interplay of factors that imbalance job demands and our ability to manage them effectively. Understanding these causes is crucial for both employees and employers to create a more supportive and healthy work environment. Some of the key factors are as follows:
Heavy workload
Being constantly bombarded with tasks and feeling overwhelmed can trigger anxiety and inadequacy. This can occur due to a lack of proper resource allocation, unrealistic expectations, or simply the nature of the job itself.
Unrealistic deadlines
Feeling pressured to meet tight deadlines can cause significant stress, especially when paired with a heavy workload or unclear expectations. This can lead to rushed work, increased error rates, and further frustration.
Long working hours
While occasional overtime might be necessary, consistently exceeding standard working hours can disrupt work-life balance, leading to physical and mental exhaustion. This fatigue can further impair our ability to manage work demands effectively, creating a vicious cycle.
Limited autonomy
Feeling like your work lacks autonomy or control over decision-making can be demotivating and stressful. This can manifest in micromanagement, rigid work processes, or limited opportunities for creative input.
Unclear expectations
When goals, roles, or responsibilities are not adequately defined, it can lead to confusion, frustration, and difficulty in prioritizing tasks effectively. This lack of clarity can contribute to feelings of inadequacy and hinder performance.
Technological issues
Constant dependence on unreliable technology or inadequate resources can be a major source of stress. Frequent software crashes, slow internet connectivity, or lack of proper training on necessary tools can hinder productivity and contribute to work frustration.
Poor communication
Ineffective communication can lead to misunderstandings, missed deadlines, and a general sense of confusion and frustration. This can occur from unclear instructions, lack of feedback loops, or simply poor communication practices within the organization.
Toxic workplace culture
A workplace culture characterized by bullying, harassment, or lack of respect can significantly impact employee well-being. This can lead to feelings of isolation, and anxiety, and even contribute to the development of mental health issues.
Lack of support
Feeling unsupported by colleagues, managers, or the organization can exacerbate work stress. This can manifest in a lack of recognition, inadequate mentorship opportunities, or simply a feeling of being alone in facing challenges.
Read more: A Guide to Managing Stress and Anxiety at the Workplace
How Work Stress Impacts Individuals
Here’s a closer look at some possible individual manifestations of these entwined forces.
Increased susceptibility to illness
Chronic stress weakens the immune system, making individuals more vulnerable to infections and illnesses such as colds, flu, and even chronic conditions like heart disease and diabetes.
Muscle tension and headaches
Stress often manifests physically through muscle tension, particularly in the neck and shoulders, leading to headaches and discomfort.
Anxiety and depression
Work stress can contribute to the development of anxiety and depression, characterized by persistent worry, feelings of hopelessness, and a loss of interest in activities once enjoyed.
Emotional exhaustion
Individuals experiencing burnout often describe feeling emotionally drained, depleted of their emotional resources, and lacking the energy to cope with daily life.
Decreased focus and concentration
The overwhelming pressure of work stress can impair cognitive function, making it difficult to concentrate, remember information, and make sound decisions.
Strained relationships with family and friends
When work stress bleeds into personal life, individuals may have less time and emotional energy to invest in relationships with loved ones. This can lead to feelings of isolation, resentment, and decreased communication.
Reduced patience and irritability
Constant stress can decrease patience and increase emotional reactivity, making individuals more likely to snap easily or engage in hurtful behavior towards loved ones.
Strategies for Combating Work Stress and Burnout
To address these issues and promote a better work environment, companies and employees can utilize a number of measures.
Promote a healthy work-life balance
Encourage employees to take breaks, utilize vacation time, and disconnect after work hours. This may involve implementing flexible work arrangements, setting clear communication boundaries, and leading by example.
Foster open communication
Establish clear and open communication channels, encouraging employees to voice concerns, offer suggestions, and feel comfortable seeking support from managers or HR. Regularly solicit feedback and actively listen to employee concerns.
Cultivate a supportive and respectful workplace
Implement policies and practices that promote respect, inclusion, and psychological safety within the workplace. Address instances of bullying or harassment swiftly and decisively. Encourage collaboration and teamwork to foster a sense of belonging and support.
Develop stress management techniques
Learn and practice relaxation techniques like mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, or progressive muscle relaxation. These can help regulate emotions, improve focus, and promote better sleep.
Practice effective time management
Develop and implement time management strategies that work for you. Prioritize tasks effectively, set realistic goals, and avoid overloading your schedule. Utilize tools like to-do lists, calendars, and time management apps to stay organized and on track.
Establish healthy boundaries
Set clear boundaries between work and personal life. Disconnect from work emails and calls outside of work hours, and resist the urge to check work messages constantly. Schedule time for relaxation and activities you enjoy.
Read more: How a better work-life balance helps keep your best employees

Conclusion
Both employers and employees have a shared responsibility in addressing work-related stress and burnout. Organizations may create a positive, healthy work environment that promotes employee well-being and maximizes productivity by cooperating and putting proactive initiatives into practice. Prioritizing mental and physical health can help people and organizations escape the grip of burnout and work-related stress, opening the door to a happier and more productive workplace.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Feeling overwhelmed at work? What are the warning signs?
Work stress can show up in your body and mind. Look for headaches, muscle tension, fatigue, changes in appetite, and sleep problems. You might also feel irritable, anxious, unfocused, overwhelmed, cynical, unmotivated, or indecisive. Changes in behavior like working late, neglecting personal needs, withdrawing socially, or relying on unhealthy coping mechanisms can also be red flags.
Q2. Work stress or burnout? How can I tell the difference?
While both stem from work pressure, work stress is temporary and can ease with rest and relaxation. Burnout is long-term exhaustion, affecting your emotions, physical health, and mental state. It’s harder to recover from burnout on your own.
Q3. Feeling overwhelmed? What can I do?
Identify what’s stressing you at work. Practice stress management techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or mindfulness. Set boundaries between work and personal life. Don’t be afraid to seek support from friends, family, colleagues, or a therapist.
Q4. How can employers prevent work stress and burnout?
Employers can create a healthy work environment by promoting work-life balance, open communication, fair workloads and deadlines, and employee well-being initiatives. They can also lead by example, setting the tone for healthy work habits.
Q5. Overcoming burnout? What are the steps?
Prioritize rest and relaxation, disconnect from work completely, and focus on self-care. Seek professional help from a therapist or counselor to develop coping mechanisms and support your recovery.



